Your Location:Home > Products > chemicals for Detergent > sodium lauryl sulfate(SLS K12)
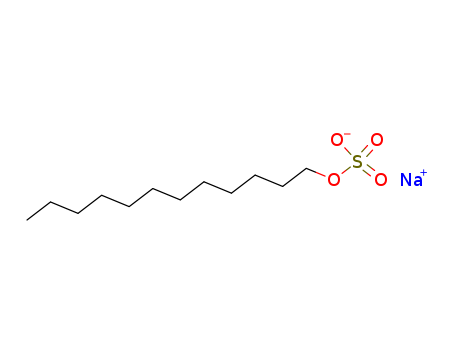


CasNo: 151-21-3
MF: C12H25NaO4S
Appearance: Clear to yellow liquid
|
Anionic surfactants |
Sodium dodecyl sulfate is an anionic surfactant, and is a typical representative of sulphate-based surfactant. It is abbreviated as SDS, and also known as AS, K12, coco alcohol sulfate, sodium lauryl sulfate and foaming agent. The commercial products are usually white to light yellow crystalline powder. It is non-toxic, slightly soluble in alcohol, insoluble in chloroform and ether, soluble in water, and has good anionic and nonionic complex compatibility. It has good emulsibility, foamability, and foaming, infiltrating, decontaminating and dispersing properties. It is abundant in foams and quickly biodegradable, and has solubility next only to fatty alcohol polyoxyethylene ether sodium sulphate (abbreviated as AES). It is not sensitive to alkali and hard water, but its stability is inferior to general sulfonate under acidic conditions and is close to AES. It is not favorable to exceed 95 °C upon long-term heating, and its irritation is at the middle level among surfactants, with an irritation index of 3.3 for a 10% solution, which is higher than AES and lower than sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate (abbreviated as LAS). Toxicity LD50 is 1300mg/kg. There is no evidence that this product is carcinogenic, but high doses may indeed irritate the skin. However, in general sanitary products the concentration is limited when used as a forming agent, and is in line with national standards. So there is no need to concern. Sodium dodecyl sulfate is a major component of detergent. It is usually used in the DNA extraction process to separate DNA after protein denaturation. It is often misread as sodium dodecyl sulfonate. It is widely used as a foaming agent in toothpaste, soap, shower gel, shampoo, detergent and cosmetics. 95% of personal care products and household cleaning products contain sodium lauryl sulfate. The above information is edited by the lookchem of Jin Yinxue. |
|
Toxicity |
It can be safely used for food, but the content of sodium lauryl sulfate should not be less than 90% (FDA, §172.822, 2000). LD50 is 1288mg/kg (rat, oral). |
|
Sodium dodecyl sulfonate |
There is certain universality of confusion and misuse for them, both of which belong to the anionic surfactants and the English abbreviations are both SDS. Sodium dodecyl sulfate (abbreviated as SDS) is also called sodium lauryl sulfate (abbreviated as SLS), belongs to sulfate salt and has a molecular weight of 288.38. It is a white or light yellow crystal, and is easily soluble in water. Sodium dodecyl sulfonate (abbreviated as SDS) belongs to sulfonate, has a molecular weight of 272.38, and differs with the structure of sodium dodecyl sulfate in that it lacks one oxygen atom and the carbon atom is directly connected to the sulfur atom. Please note the difference so as to avoid misuse. |
|
Utilization limitation |
(FDA, §172.822, 2000, mg/kg): dry protein 1000; frozen protein 125; liquid protein 125; marshmallow foaming agent used in an amount of 0.5% gelatin; as a surfactant for solid drinks acidified with fumaric acid and juice drinks acidified with fumaric acid, 25; as moisturizers for grease, 10 (amount of grease). According to the regulation of (FDA, §172.210, 2000), it can be used as a citrus fruit surface coating agent, and the amount is limited per GMP. |
|
Chemical property |
It is a white to pale yellow powder, has a slight special smell, and is easily soluble in water. |
|
Production method |
Sulphur trioxide method: the reaction apparatus is a vertical reactor. At 32 °C nitrogen gas is introduced into the reactor through the gas vents at a flow rate of 85.9 L·min-1. At 82.7 kPa lauryl alcohol is introduced at a flow rate of 58 g·min-1. The liquid sulfur trioxide is fed into flash evaporator at 124.1 kPa, the flash temperature is maintained at 100 °C, and sulfur trioxide flow rate is controlled to be 0.907 2 kg·h-1. Sulfated product is then rapidly quenched to 50 °C, injected into the aging device and left for 10 to 20 min, and finally injected into the neutralization kettle and neutralized with a base. The neutralizing temperature is controlled at 50 °C. The material is discharged when the pH value is adjusted to 7 to 8.5, to obtain a liquid product which is spray dried to give a solid product. Batch method: lauryl alcohol is charged into reaction kettle and pre-heated to 30 °C. Then chlorosulfonic acid 0.03 mol in excess than the theoretical amount is sprayed into the alcohol under high speed agitation. The reaction temperature was controlled at 30 to 35 °C. After the sulfation reaction, it is injected into the neutralization kettle and neutralized with 30% lye to a pH value of 7 to 8.5, and finally bleached with 0.4% (weight) hydrogen peroxide. It is spray dried to give a solid. It can also be formulated into solutions according to quality standard. Continuous method: the reaction apparatus is tubular reactor. Lauryl alcohol is initially saturated with hydrogen chloride. Lauryl alcohol at a flow rate of 334 g·min-1 and hydrogen chloride at a flow rate of 40.5 g·min-1 are fed into saturation chamber through gauge. Then the solution of lauryl alcohol with hydrogen chloride is fed into reactor at 21.4 °C to react with chlorosulfonic acid. After the reaction is subjected to gas-liquid separation, the sulfated product flows from the bottom of the separator into neutralization kettle. It is neutralized with 30% sodium hydroxide at 50 °C to give a liquid product, which is spray dried to give a solid product. |
|
Production Methods |
Sodium lauryl sulfate is prepared by sulfation of lauryl alcohol, followed by neutralization with sodium carbonate. |
|
Air & Water Reactions |
Insoluble in water. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
DODECYL SULFATE is incompatible with strong oxidizers. Sodium dodecyl sulfate is also incompatible with cationic materials and with acids with pH below 2.5. Salts, basic, such as DODECYL SULFATE, are generally soluble in water. The resulting solutions contain moderate concentrations of hydroxide ions and have pH's greater than 7.0. They react as bases to neutralize acids. These neutralizations generate heat, but less or far less than is generated by neutralization of the bases in reactivity group 10 (Bases) and the neutralization of amines. They usually do not react as either oxidizing agents or reducing agents but such behavior is not impossible. |
|
Health Hazard |
Inhalation of dust causes sneezing and coughing. Ingestion of large amounts causes irritation of stomach. Dust irritates eyes and may cause burns on prolonged contact. Contact with skin causes some irritation; continued exposure to water solution causes drying out and cracking. |
|
Fire Hazard |
Flash point data for Sodium dodecyl sulfate are not available; however, Sodium dodecyl sulfate is probably combustible. |
|
Pharmaceutical Applications |
Sodium lauryl sulfate is an anionic surfactant employed in a wide range of nonparenteral pharmaceutical formulations and cosmetics.It is a detergent and wetting agent effective in both alkaline and acidic conditions. In recent years it has found application in analytical electrophoretic techniques: SDS (sodium dodecyl sulfate) polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis is one of the more widely used techniques for the analysis of proteins; and sodium lauryl sulfate has been used to enhance the selectivity of micellar electrokinetic chromatography (MEKC). |
|
Contact allergens |
This anionic detergent is widely used in cosmetics and industry. As a skin irritant agent, SLS can be used in several dermatological applications. It is also a good indicator of excited skin during patch testing. |
|
Biochem/physiol Actions |
Sodium dodecyl sulphate?(SDS) helps to quickly disrupt the biological membranes. It is usually used as one of the major constituent of several reagents, that are used to purify nucleic acids. SDS can block the activity of RNase and deoxyribonuclease (DNase). |
|
Safety Profile |
Poison by intravenous and intraperitoneal routes. Moderately toxic by ingestion. An experimental teratogen. A human skin irritant. An experimental eye and severe skin irritant. A mild allergen. Mutation data reported. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of SO, and Na2O. See also ESTERS and SULFATES. |
|
Safety |
Sodium lauryl sulfate is widely used in cosmetics and oral and topical pharmaceutical formulations. It is a moderately toxic material with acute toxic effects including irritation to the skin, eyes, mucous membranes, upper respiratory tract, and stomach. Repeated, prolonged exposure to dilute solutions may cause drying and cracking of the skin; contact dermatitis may develop.(3) Prolonged inhalation of sodium lauryl sulfate will damage the lungs. Pulmonary sensitization is possible, resulting in hyperactive airway dysfunction and pulmonary allergy. Animal studies have shown intravenous administration to cause marked toxic effects to the lung, kidney, and liver. Mutagenic testing in bacterial systems has proved negative. Adverse reactions to sodium lauryl sulfate in cosmetics and pharmaceutical formulations mainly concern reports of irritation to the skin or eyes following topical application. Sodium lauryl sulfate should not be used in intravenous preparations for humans. The probable human lethal oral dose is 0.5–5.0 g/kg body-weight. LD50 (mouse, IP): 0.25 g/kg LD50 (mouse, IV): 0.12 g/kg LD50 (rat, oral): 1.29 g/kg LD50 (rat, IP): 0.21 g/kg LD50 (rat, IV): 0.12 g/kg |
|
storage |
Sodium lauryl sulfate is stable under normal storage conditions. However, in solution, under extreme conditions, i.e. pH 2.5 or below, it undergoes hydrolysis to lauryl alcohol and sodium bisulfate. The bulk material should be stored in a well-closed container away from strong oxidizing agents in a cool, dry place. |
|
INDEX/GRADE |
SPECIFICATION |
|
Active matter |
92% min |
|
Petroleum eth soluble substances |
1.5% max |
|
Inorganic salts (NaCl+Na 2 SO 4 ) |
5.5% max |
|
Water |
5.0% max |
|
pH value (1% aq. solution) |
7.5-9.5 |
|
Whiteness (WG) |
80 min |
|
Heavy metal |
20ppm max |
|
As |
3ppm max |
|
Purification Methods |
Purify this detergent by Soxhlet extraction with pet ether for 24hours, followed by dissolution in acetone/MeOH/H2O 90:5:5(v/v) and recrystallisation [Politi et al. J Phys Chem 89 2345 1985]. It has been purified by two recrystallisations from absolute EtOH, aqueous 95% EtOH, MeOH, isopropanol or a 1:1 mixture of EtOH/isopropanol to remove dodecanol, and dried under vacuum [Ramesh & Labes J Am Chem Soc 109 3228 1987]. SDS has also been purified by repeatedly foaming whereby a 0.15% aqueous solution is made to foam and the foam is discarded, then the H2O is removed in vacuo and the residue is diluted to the required concentrations [see Cockbain & McMullen Trans Faraday Soc 47 322 1951] or by liquid-liquid extraction [see Harrold J Colloid Sci 15 280 1960]. Dry it over silica gel. For DNA work it should be dissolved in excess MeOH passed through an activated charcoal column and evaporated until it crystallises out. It has also been purified by dissolving in hot 95% EtOH (14mL/g), filtering and cooling, then drying in a vacuum desiccator. Alternatively, it is crystallised from H2O, vacuum dried, washed with anhydrous Et2O and dried in vacuum again. These operations are repeated five times [Maritato J Phys Chem 89 1341 1985, Lennox and McClelland J Am Chem Soc 108 3771 1986, Dressik J Am Chem Soc 108 7567 1986]. [Beilstein 1 IV 1847.] |
|
Incompatibilities |
Sodium lauryl sulfate reacts with cationic surfactants, causing loss of activity even in concentrations too low to cause precipitation. Unlike soaps, it is compatible with dilute acids and calcium and magnesium ions. Sodium lauryl sulfate is incompatible with salts of polyvalent metal ions, such as aluminum, lead, tin or zinc, and precipitates with potassium salts. Solutions of sodium lauryl sulfate (pH 9.5–10.0) are mildly corrosive to mild steel, copper, brass, bronze, and aluminum. |
|
Regulatory Status |
GRAS listed. Included in the FDA Inactive Ingredients Database (dental preparations; oral capsules, suspensions, and tablets; topical and vaginal preparations). Included in nonparenteral medicines licensed in the UK. Included in the Canadian List of Acceptable Non-medicinal Ingredients. |
|
Chemical Composition and Structure |
Sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS or NaDS), also known as sodium lauryl sulfate (SLS), is an anionic surfactant belonging to the alkyl sulfates surfactants. It consists of a 12-carbon atom chain (dodecyl group) attached to a sulfate group, giving it an amphiphilic structure. SDS is synthesized from dodecyl alcohol through a reaction with sulfuric acid, resulting in the formation of dodecyl sulfate, which is then converted to sodium salt using sodium hydroxide. |
|
Corrosion Inhibition |
SDS serves as an efficient corrosion inhibitor for materials such as AZ91 Mg alloy by adsorbing on AlMn intermetallics to suppress micro-galvanic corrosion. |
|
Emulsion Stabilization |
SDS is utilized in the crosslinking of gelatin, where it modifies the surface structure and charge of emulsion droplets by forming electrostatic complexes. This process results in desirable droplet structures with high stability. |
|
Foaming Agent |
SDS is widely employed as a foaming agent in various fields due to its low cost and excellent foaming ability. |
|
Stabilizer for Fabrication of Magnetic Nanoparticles (MNPs) |
SDS is used as a stabilizer in the fabrication of MNPs, and these nanoparticles find applications as antibacterial and antifungal agents. |
|
Effects of Metal Ions on Aggregation Behavior |
Sodium dodecyl sulfate's aggregation behavior is influenced by the presence of metal ions such as Europium(III) and Cerium(III). Additionally, the addition of sodium ions to SDS solutions alters critical micelle concentration (CMC) values, with CMC decreasing as the concentration of sodium salts like NaCl, sodium acetate, and sodium propionate increases. |
|
Definition |
An anionic surfactant, usually a mixture of sodium alkyl sulfates that lowers surface tension of aqueous solutions. |
|
General Description |
White to pale yellow paste or liquid with a mild odor. Sinks and mixes with water. |
|
Properties and Applications |
INDEX/GRADE SPECIFICATION Appearance Needle form without hard lumps Active matter 92% min Petroleum eth soluble substances 1.5% max Inorganic salts (NaCl+Na 2 SO 4 ) 5.5% max Water 5.0% max pH value (1% aq. solution) 7.5-9.5 Whiteness (WG) 80 min Heavy metal 20ppm max As 3ppm max |
|
Appearance |
Needle form without hard lumps |
InChI:InChI=1/C24H50O4S.Na/c1-3-5-7-9-11-13-15-17-19-21-23-27-29(25,26)28-24-22-20-18-16-14-12-10-8-6-4-2;/h3-24H2,1-2H3;/q;+1
The present invention relates to method ...
Metal dodecyl sulfates of trivalent alum...
A series of cosmetic scrubs and creams, ...
The present invention relates to a formu...


1-Hexadecanol
sodium dodecyl-sulfate
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
|


sodium dodecyl-sulfate


hexan-1-ol
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
|

1-dodecyl alcohol
lauric acid

tris(dodecyloxy)borane

dodecyl 4-methylphenyl sulfide
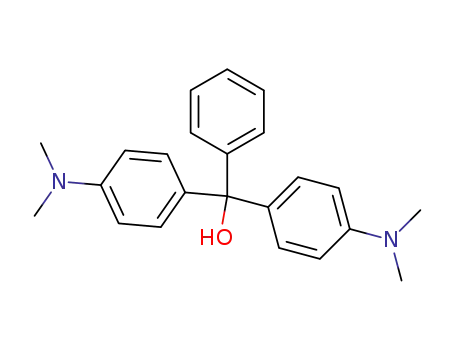
1,1-bis(4-dimethylaminophenyl)-1-phenyl-methanol
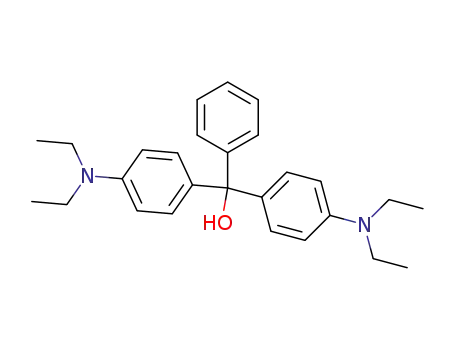
brilliant green
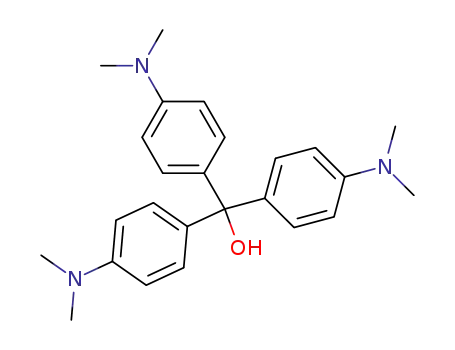
crystal violet carbinol base