Your Location:Home > Products > chemicals for Printing and dyeing > Sodium acetate
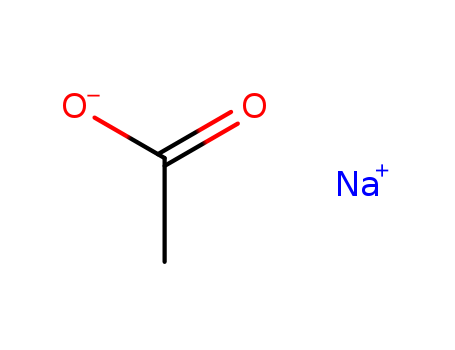


CasNo: 127-09-3
MF: C2H3NaO2
Appearance: white powder
|
Chemical Description |
Sodium acetate is a salt commonly used as a buffer in biochemistry. |
|
Physical properties |
Anhydrous salt is a colorless crystalline solid; density 1.528 g/cm3; melts at 324°C; very soluble in water; moderately soluble in ethanol. The colorless crystalline trihydrate has a density 1.45 g/cm3; decomposes at 58°C; is very soluble in water; pH of 0.1M aqueous solution is 8.9; moderately soluble in ethanol, 5.3 g/100mL. |
|
Preparation |
Sodium acetate is prepared by reacting sodium hydroxide or sodium carbonate with acetic acid in aqueous solution. The solution is evaporated to obtain hydrated crystals of sodium acetate. NaOH + CH3COOH → CH3COONa + H2O Na2CO3 + CH3COOH → 2CH3COONa + CO2 + H2O |
|
Definition |
A white solid prepared by the neutralization of ethanoic acid with either sodium carbonate or sodium hydroxide. Sodium ethanoate reacts with sulfuric acid to form sodium hydrogensulfate and ethanoic acid; with sodium hydroxide it gives rise to sodium carbonate and methane. Sodium ethanoate is used in the dyeing industry. |
|
Application |
2 - 1 - Industrial Sodium acetate is used in the textile industry to neutralize sulfuric acid waste streams, and as a photoresist while using aniline dyes. It is also a pickling agent in chrome tanning, and it helps to retard vulcanization of chloroprene in synthetic rubber production. In processing cotton for disposable cotton pads, sodium acetate is used to eliminate the buildup of static electricity. 2 - 2 - Concrete longevity Sodium acetate is used to reduce the damage water can potentially do to concrete by acting as a concrete sealant, while also being environmentally benign and cheaper than the epoxy alternative that is usually employed for sealing concrete against water permeation. 2 - 3 - Food Sodium acetate may be added to foods as a seasoning. It may be used in the form of sodium diacetate — a 1:1 complex of sodium acetate and acetic acid, given the E-number E262. A frequent use is to impart a salt and vinegar flavor to potato chips. 2 - 4 - Buffer solution As the conjugate base of acetic acid, a solution of sodium acetate and acetic acid can act as a buffer to keep a relatively constant pH. 2 - 5 - Heating pad Sodium acetate is also used in consumer heating pads or hand warmers and is also used in hot ice. Sodium acetate trihydrate crystals melt at 58.4°C , (to 58°C ) dissolving in their water of crystallization. When they are heated to around 100°C, and subsequently allowed to cool, the aqueous solution becomes supersaturated. This solution is capable of cooling to room temperature with out forming crystals. |
|
Synthesis |
For laboratory use, sodium acetate is very inexpensive, and is usually purchased instead of being synthesized. It is sometimes produced in a laboratory experiment by the reaction of acetic acid (ethanoic acid) with sodium carbonate, sodium bicarbonate, or sodium hydroxide. These reactions produce aqueous sodium acetate and water. Carbon dioxide is produced in the reaction with sodium carbonate and bicarbonate, and it leaves the reaction vessel as a gas (unless the reaction vessel is pressurized). This is the well-known "volcano" reaction between baking soda (sodium bicarbonate) and vinegar. CH3COOH + NaHCO3 → CH3COONa + H2O + CO2 Industrially, sodium acetate is prepared from glacial acetic acid and sodium hydroxide. CH3COOH + NaOH → CH3COONa + H2O. |
|
Reactions |
Sodium acetate can be used to form an ester with an alkyl halide such as bromo ethane: CH3COONa + Br CH2CH3→ CH3COOCH2CH3+ NaBr Caesium salts catalyze this reaction. |
|
General Description |
Sodium Acetate is reported to inhibit the growth of Listeria monocytogenes. |
|
Reactivity Profile |
When sodium acetate reacts with strong acids, irritating, noxious vapors of acetic acid are usually produced. Sodium acetate is sufficiently basic to catalyze the violent polymerization of diketene, perhaps as well as other reactive dimers that are susceptible to polymerization in the presence of a mild base. |
|
Flammability and Explosibility |
Nonflammable |
|
Biological Activity |
Commonly used laboratory reagent |
|
Safety Profile |
Poison by intravenous route. Moderately toxic by ingestion. A skin and eye irritant. Migrates to food from packagmg materials. Violent reaction with F2, m03, diketene. When heated to decomposition it emits toxic fumes of Na2O. |
|
Purification Methods |
Crystallise it from acetic acid and keep it under vacuum for 10hours at 120o. Alternatively, it is crystallised from aqueous EtOH, as the trihydrate. This material can be converted to anhydrous salt by heating slowly in a porcelain, nickel or iron dish, so that the salt liquefies. Steam is evolved and the mass again solidifies. Heating is now increased so that the salt melts again. (NB: if it is heated too strongly, the salt can char; avoid this.) After several minutes, the salt is allowed to solidify and is cooled to a convenient temperature (in a desiccator) before being powdered and bottled. The water content should now be less than 0.02%. [Beilstein 2 II 113, 2 III 184, 2 IV 109.] |
InChI:InChI=1/C2H4O2.Na.3H2O/c1-2(3)4;;;;/h1H3,(H,3,4);;3*1H2/q;+1;;;/p-1
Cu(II), Fe(II), Co(II), Ni(II), Mn(II) c...
A new, very efficient and elegant proced...
A polyoxometalate (POM) assisted approac...
We report herein a series of Cp*Ir compl...
Twenty new complexes of hydroxyaryltellu...
The use of bio-renewable resources for t...
Cobalt(II) and copper(II) complexes with...
A facile fluorescent method was develope...
Electrooxidation of ethanol on a polycry...
The use of bio-renewable resources, such...
-
-
The alkaline hydrolysis of p-nitrophenyl...
Effect and cause: Secondary deuterium is...
The new tri-enaminone, namely, 3,4-bis(3...
The oxidation kinetics of methyl vinyl k...
We experimentally demonstrate that super...
In this work, new evidence for the photo...
Disclosed herein are compounds useful fo...
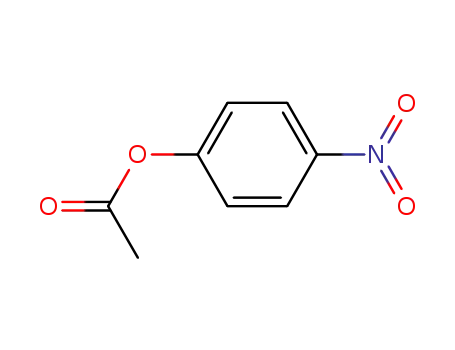
4-nitrophenol acetate

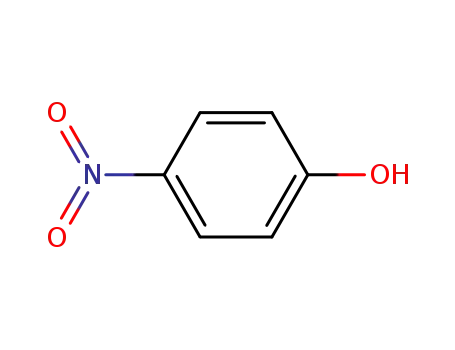
4-nitro-phenol
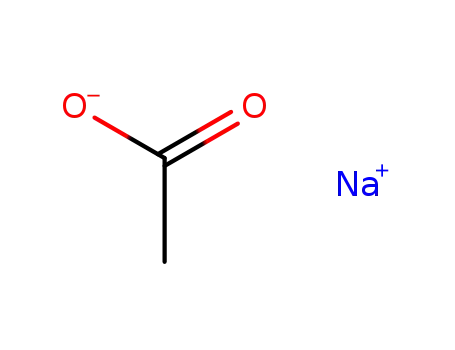
sodium acetate
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; dibenzo-18-crown-6;
In
toluene;
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
var. alkali, var. catalyst;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; dibenzo-18-crown-6; tetraethylammonium bromide; water;
In
toluene;
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
influence of alkali, phase-transfer catalyst, water, methanol;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; 18-crown-6 ether;
In
benzene;
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; 18-crown-6 ether;
In
toluene;
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; 18-crown-6 ether;
In
xylene;
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; 18-crown-6 ether;
In
hexane;
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; 18-crown-6 ether;
In
cyclohexane;
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; 18-crown-6 ether;
In
1,4-dioxane;
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; 18-crown-6 ether;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; 18-crown-6 ether;
In
tetrachloromethane;
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; 18-crown-6 ether;
In
various solvent(s);
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; 18-crown-6 ether;
In
chlorobenzene;
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; tetraethylammonium bromide;
In
benzene;
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; tetraethylammonium bromide;
In
toluene;
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; tetraethylammonium bromide;
In
xylene;
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; tetraethylammonium bromide;
In
hexane;
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; tetraethylammonium bromide;
In
cyclohexane;
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; tetraethylammonium bromide;
In
1,4-dioxane;
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; tetraethylammonium bromide;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; tetraethylammonium bromide;
In
tetrachloromethane;
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; tetraethylammonium bromide;
In
benzonitrile;
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; tetraethylammonium bromide;
In
chlorobenzene;
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; tetraethylammonium bromide;
In
various solvent(s);
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; 18-crown-6 ether; tetraethylammonium bromide;
In
various solvent(s);
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; 18-crown-6 ether; tetraethylammonium bromide;
In
xylene;
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; 18-crown-6 ether; tetraethylammonium bromide;
In
chlorobenzene;
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; 18-crown-6 ether; tetraethylammonium bromide;
In
benzonitrile;
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; 18-crown-6 ether; tetraethylammonium bromide;
In
tetrachloromethane;
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; 18-crown-6 ether; tetraethylammonium bromide;
In
tetrahydrofuran;
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; 18-crown-6 ether; tetraethylammonium bromide;
In
1,4-dioxane;
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; 18-crown-6 ether; tetraethylammonium bromide;
In
cyclohexane;
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; 18-crown-6 ether; tetraethylammonium bromide;
In
hexane;
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; 18-crown-6 ether; tetraethylammonium bromide;
In
toluene;
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
|
|
With
sodium hydroxide; 18-crown-6 ether; tetraethylammonium bromide;
In
benzene;
at 25 ℃;
Rate constant;
|
|
|
With
N-hexadecyl-N-(2-hydroxyethyl)-N,N-dimethylammonium bromide; sodium hydroxide;
In
water;
at 25 ℃;
pH=9.2;
Concentration;
Reagent/catalyst;
Kinetics;
Micellar solution;
|
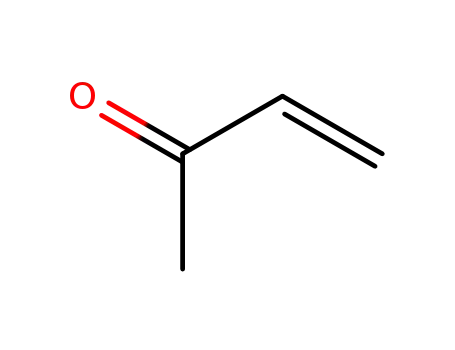
methyl vinyl ketone

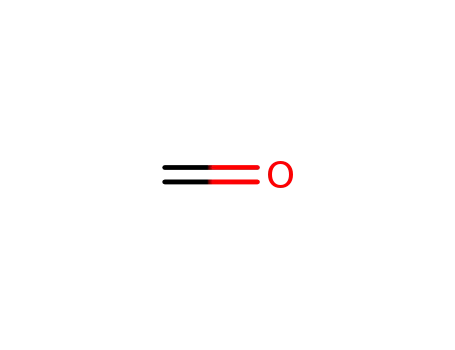
formaldehyd


sodium acetate
| Conditions | Yield |
|---|---|
|
With
chloroamine-T;
In
sodium hydroxide;
at 35 ℃;
for 48h;
Kinetics;
Mechanism;
Rate constant;
ΔE(excit.), ΔS(excit.); different temperatures;
|
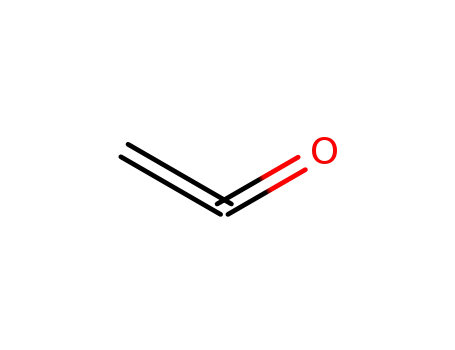
Ketene
tetrachloromethane
diethoxymethyl acetate
diethyl ether
(2-hydroxyethyl)(methyl)amine
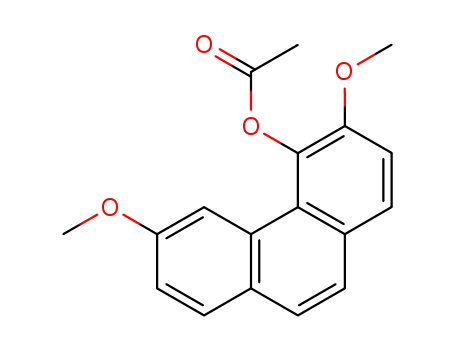
3,6-Dimethoxy-4-acetoxyphenanthrene
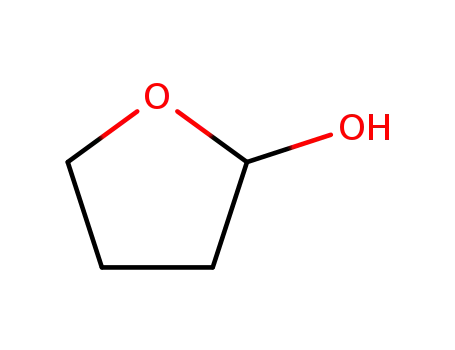
2-hydroxytetrahydrofuran
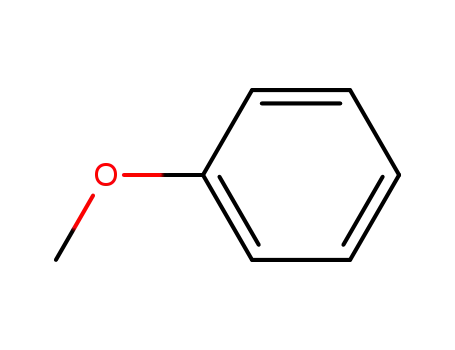
methoxybenzene